Mushrooms with a delicate taste and fleshy texture are popular and often used in the kitchen for various dishes.
Traditionally, mushrooms are most often eaten after heat treatment, such as boiling, frying, stewing, or baking, but does this mean that they can't be eaten raw? Is it dangerous to eat mushrooms without heat treatment?
It turns out that eating raw mushrooms can harm us. In this article, we will look at the advantages and disadvantages of eating raw mushrooms. Focusing on the latter, we will conduct research and consider the risks to the body.
There will also be no shortage of tips on how to safely prepare mushrooms for consumption.
Benefits of eating mushrooms raw
The first advantage that raw mushrooms give us is the peculiar richness of nutrients.
Raw mushrooms rich in vitamins and mineralssuch as potassium, copper, selenium, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, and vitamin D. In addition, they are sources of fiber and protein that are essential for the proper functioning of the body.
Heat treatment of mushrooms means that they can lose some of their minerals and vitamins, as well as other valuable nutrients.
We also get fresh taste - Raw mushrooms have a delicate, refreshing taste, which distinguishes them from mushrooms that have undergone heat treatment. This is an attractive option in the kitchen for many people.
What is the most popular form of serving raw mushrooms? Raw mushroom salad
The most popular recipe is a salad with raw mushrooms, which consists of:
- 10 raw mushrooms
- 4 hard-boiled eggs
- peeled cucumber
- 2 teaspoons mayonnaise
- fresh dill
- salt
- pepper
Danger of eating champignons without heat treatment
And now we move on to this less pleasant part. The topic is not fresh-already in 2002, a work was published from which we can learn interesting things.
More and more data is coming from experimental animal studies and studies in vitroWhat are mushrooms per se and phenylhydrazine derivatives in mushrooms have adverse health effects after prolonged and frequent oral exposure.
Toth and his colleagues showed that lifelong feeding of Swiss albino mice raw, fried in dry form, and also freeze-dried A. bisporus (i.e., a common mushroom), as well as three of the four phenylhydrazine derivatives, cause tumors in animals (Toth 2000, Andersson and GRE 2002). Agaritin was the only phenylhydrazine ingredient A. bisporus, which is negative in such studies (Toth et al. 1981).
Until it is determined whether the consumption of biologically significant amounts of cultivated mushrooms is an acceptable risk of adverse health effects or not, it seems appropriate abstaining from excessive exposure to phenylhydrazines.
In order not to be too intimidating, there are other risks and disadvantages of eating mushrooms raw. These include:
- Difficulty digesting champignons! These mushrooms contain chitin, a compound found in the cell walls of fungi. The digestive system has difficulty digesting chitin, which is a polysaccharide. Eating raw mushrooms can cause bloating or a heavy stomach, especially in people with sensitive digestive systems. As a result, the stomach tolerates boiled or baked mushrooms better.
- Risk of infection! Bacteria, parasites, or fungi present on the surface of raw mushrooms can cause infection. Therefore, avoid mushrooms that appear spoiled or stale, always washing them thoroughly before eating.
- Toxins! Be careful when picking wild mushrooms. When collecting wild mushrooms, you risk confusing them with similar but poisonous species. Collecting wild mushrooms requires special knowledge and caution, as eating poisonous wild mushrooms can lead to serious poisoning.
- Allergic reactions + intolerance! Some people may be allergic to mushroom protein, which can cause allergies. People who are allergic to mushrooms should avoid mushrooms, both raw and cooked.
Does the ban on eating raw mushrooms apply to all types of mushrooms?
Yes, because of the agaritin content, you can not eat any types of mushrooms, including white, brown or Portobello.
Can I eat raw mushrooms during pregnancy?
Do not eat raw mushrooms during pregnancy. This is due to the content of agaritin and chitin. Prolonged exposure to agaritin can negatively affect your health, and chitin can cause digestive problems.
How to eat mushrooms safely?
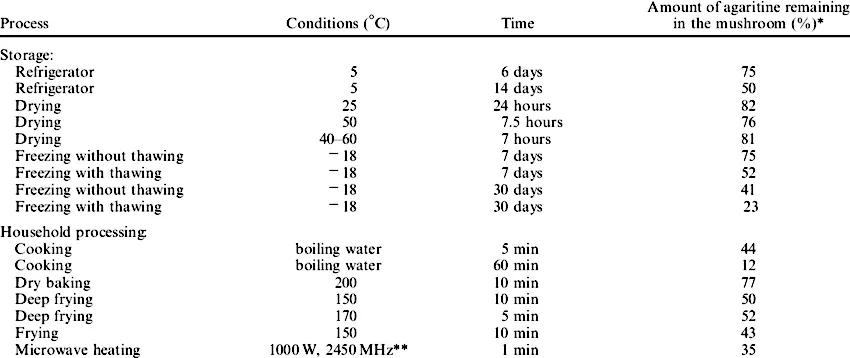
For safe consumption of champignons, they must be subjected to heat treatment before use. Depending on the method and time used, the content of dangerous agaritin in mushrooms will significantly decrease.
A microwave oven is best for this purpose. However, a minute of the action of microwaves will deprive the mushrooms of 65% of the harmful substance content. Reducing agaritin by 56 percentage points will ensure 5-minute mushroom preparation. We will achieve a very similar effect by frying mushrooms for 10 minutes. The content of the unwanted ingredient decreased by 57 percentage points in the study.
Even freezing mushrooms for 7 days and thawing them before eating resulted in a reduction in the phenylhydrazine derivative by almost half. Drying or storing mushrooms in the refrigerator also negates the agaritin content of the product. You can see the exact results (the effect of time and method on the level of bad agaritin in mushrooms) in the table below:
Can I freeze raw mushrooms?
Yes, raw mushrooms can be frozen. Before you freeze them, make sure they are well washed and dried. If they are cleaned, they can be used without defrosting for various dishes. Interestingly, long-term freezing of mushrooms will get rid of a significant part of harmful agaritin.
Can I put raw mushrooms on pizza?
Yes, you can use raw mushrooms by adding them as pizza toppings. However, don't forget to wash and dry the mushrooms before freezing them. Mixing different ways to prepare champignons allows you to remove more unwanted agaritin from them.
Literature
Schulzová, V., Hajšlová, J., Peroutka, R., Gry, J., & Andersson, H. C. (2002). Influence of storage and household processing on the agaritine content of the cultivated Agaricus mushroom. Food Additives & Contaminants, 19(9), 853-862.
Toth, B. (2003). Hydrazines and cancer: A guidebook on the carciognic activities of hydrazines, related chemicals, and hydrazine containing natural products. CRC Press.
Toth, B., Erickson, J., Gannett, P., & Patil, K. (1997). Carcinogenesis by the cultivated baked Agaricus bisporus mushroom in mice. Oncology Reports, 4(5), 931-936.
Toth, B., Raha, C. R., Wallcave, L., & Nagel, D. (1981). Attempted tumor induction with agaritine in mice. Anticancer Research, 1(5), 255-258.